What are AI Agents in Dynamics 365 Business Central?

Artificial intelligence is becoming more practical inside ERP systems, and Dynamics 365 Business Central is no exception. Microsoft is introducing AI agents to help organizations manage growing transaction volumes, reduce manual work, and improve consistency across finance and operations. To use them effectively, it is important to understand what AI agents in Business Central are, how they work, and where they add value compared to traditional automation and Copilot.
What is Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central?
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) system designed for growing and mid-market organizations. It brings core business functions into a single platform, including finance, supply chain management, inventory, sales, purchasing, and project operations. Because it is part of the broader Dynamics 365 ecosystem, Business Central connects natively with applications such as Microsoft 365, Power BI, Power Platform, and other Dynamics 365 apps, enabling consistent data flow across the organization.
Beyond core ERP functionality, Business Central is built to support operational efficiency and informed decision-making. The platform includes embedded reporting, role-based dashboards, and configurable workflows that reflect how teams actually work. Increasingly, Business Central relies on embedded intelligence and automation to reduce manual effort, surface insights from data, and support faster, more accurate business processes across finance and operations.
What are AI agents in Business Central?
AI agents in Business Central are intelligent, autonomous software assistants that can perform or assist with business processes using artificial intelligence. They are a new class of functionality within Business Central that goes beyond standard rule-based automation or static workflows. Built using Microsoft’s Copilot and related AI services, these agents are designed to understand context, interact in natural language, and make decisions to carry out tasks on behalf of users. Unlike traditional automation, which follows fixed rules and predefined triggers, AI agents can adapt their behavior based on patterns, exceptions, and changing conditions in the data. In Business Central, these agents operate within the platform to assist with operational, financial, and administrative tasks, supporting users rather than replacing them.
AI agents in Business Central are closely related to Copilot and the Power Platform. Copilot provides the conversational and generative AI layer that users interact with, while AI agents extend those capabilities by performing background actions, monitoring transactions, and initiating workflows. Through Power Automate, Power Apps, and Dataverse, AI agents can work across Business Central and connected systems. Examples include reviewing transactions for anomalies, drafting and posting routine journal entries, suggesting actions to resolve exceptions, following up on overdue items, or preparing summaries for review before execution.
Benefits of AI agents in Business Central
- Reduced manual effort and operational overhead by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks
- Faster, more consistent decision-making based on real-time data and learned patterns
- Improved data accuracy and visibility through continuous monitoring and validation
- Greater scalability as transaction volumes increase without adding administrative burden
- Better use of staff time by shifting focus from routine processing to higher-value analysis and oversight

Evaluate AI agents for Business Central
Rand Group helps organizations identify where AI agents add value and align them with existing Business Central processes. The result is practical automation that supports users without adding risk.
How AI agents work in Business Central
AI agents in Business Central operate by combining your business data with advanced AI logic to drive actions. They work by combining data awareness, event detection, and guided decision-making inside the ERP platform. They continuously evaluate structured data from Business Central, including financial entries, sales and purchasing documents, inventory movements, and master records. In addition, AI agents can use data from connected systems through Dataverse, the Power Platform, and Microsoft 365, which provides broader business context across departments.
At a practical level, AI agents in Business Central follow a repeatable operating model that balances automation with oversight:
- Data sources: Core Business Central tables, historical transaction data, and connected application data provide the foundation for analysis.
- Triggers: Events such as new transactions, exceptions, time-based schedules, or threshold breaches activate the agent.
- Decision logic: AI models evaluate patterns, context, and confidence levels instead of relying only on static rules.
- Actions: The agent may flag issues, prepare transactions, launch workflows, or generate recommendations. Actions can be fully automated or require user approval.
- User interaction: Copilot surfaces insights, explanations, and suggested actions, allowing users to review and intervene when needed.
This structure allows AI agents in Business Central to scale across high transaction volumes while maintaining control, auditability, and alignment with business policies.
AI agents available in Business Central today
Microsoft has begun introducing AI agents as built-in capabilities within Business Central, focusing on scenarios where consistency, scale, and reduced manual review matter most. These agents are designed to assist users in high-volume processes rather than fully automate decisions. Today, the most common examples focus on sales order processing and payables, with broader expansion underway.
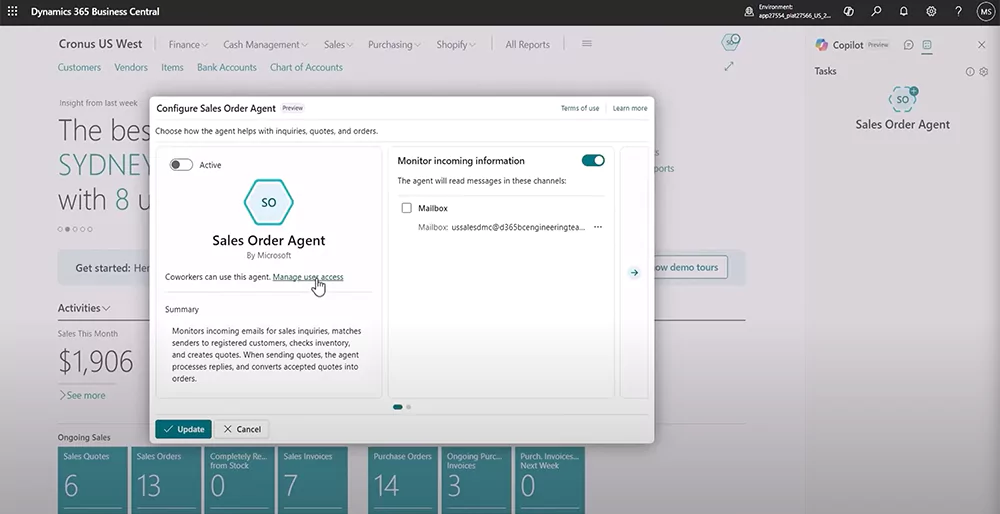
Sales order agent
The Sales Order Agent in Business Central is designed to automate the intake and processing of sales orders received by email. It monitors a shared inbox, interprets customer requests, and builds sales quotes using real-time data from Business Central. The agent handles the full sequence from email intake through quote creation, while keeping users in control through required approvals before anything is sent or posted.
Key capabilities of the Sales Order Agent include:
- Monitoring a shared email inbox for customer requests for quotes or orders
- Identifying customers by matching sender information to Business Central records
- Interpreting product requests, even when descriptions are vague or non-standard
- Searching inventory and validating item availability and delivery dates
- Creating complete sales quotes with pricing, taxes, and delivery details
- Drafting professional, branded email responses with PDF quotes attached
- Routing quotes for human review and approval before sending
- Converting approved quotes into sales orders and preparing order confirmations
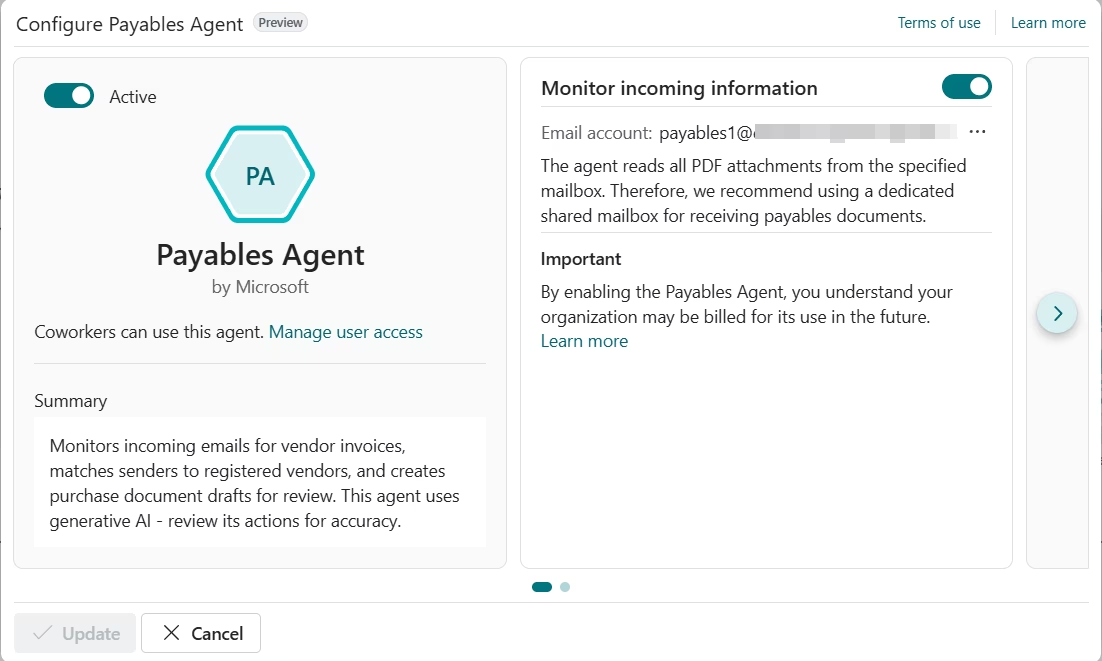
Payables agent
The Payables Agent in Business Central automates the intake and preparation of vendor invoices by monitoring a designated mailbox, analyzing invoice PDFs, and creating draft purchase invoices for review. It is designed to reduce accounts payable bottlenecks by applying accounting context and historical data to invoice registration, while requiring minimal setup beyond configuration and activation. Users review and approve invoice drafts before posting, ensuring accuracy, control, and auditability as invoice volumes increase.
Key capabilities of the Payables Agent include:
- Monitoring mailboxes for incoming vendor invoice emails
- Importing invoice PDFs into Inbound E-Documents automatically
- Extracting invoice details using AI-based document analysis
- Creating draft purchase invoices based on invoice content and prior history
- Processing multiple invoice attachments from a single email separately
- Routing invoices for user review, approval, and posting
Custom AI agents
Beyond Microsoft-delivered agents, organizations can create custom AI agents tailored to their own processes. Using the Power Platform, these agents can work directly with Business Central data and connected systems. This approach allows teams to extend AI agent functionality to industry-specific or role-specific scenarios.
Options for building custom AI agents include:
- Copilot Studio: Designing conversational or task-based agents for specific business roles
- AI Builder: Applying models for document processing, prediction, and classification
- Power Automate and Dataverse: Triggering workflows, connecting systems, and enforcing business logic
This mix of out-of-the-box and custom AI agents in Business Central allows organizations to adopt AI gradually while keeping automation aligned with real operational needs and governance requirements.
Common use cases for AI agents in Business Central
AI agents in Business Central can potentially be applied anywhere you have repetitive processes, decision rules, or lots of data to crunch. They are most effective in areas where transaction volume is high, patterns repeat, and timely action matters. They support teams by monitoring data, identifying issues, and assisting with routine decisions across finance and operations. Rather than replacing users, AI agents in Business Central help reduce friction in day-to-day work and improve consistency as the system scales.
Common use cases for AI agents in Business Central include:
- Finance and accounting: Reviewing journal entries, monitoring payables and receivables, flagging anomalies, and supporting close activities.
- Supply chain and inventory: Tracking inventory levels, identifying demand or replenishment risks, and highlighting unusual movements or variances.
- Sales and customer management: Assisting with sales order review, follow-ups, pricing checks, and customer account monitoring.
- Operations and reporting: Preparing summaries, surfacing key metrics, and supporting management reporting with up-to-date insights.
- Exception handling and proactive alerts: Detecting outliers, missed approvals, or threshold breaches and notifying users before issues escalate.
AI agents vs. Copilot in Business Central
Copilot and AI agents play distinct roles within Business Central, even though they often work together. Copilot focuses on assisting users through natural language interaction, helping them understand data, generate content, and navigate the system more efficiently. AI agents, on the other hand, are designed to handle work in the background by monitoring data and executing tasks with limited human involvement. This separation allows Business Central to support both interactive guidance and operational automation.
Pricing and cost of AI agents in Business Central
AI agents in Business Central use a consumption-based pricing model tied to Microsoft Copilot Credits. Rather than a fixed license fee per agent, organizations pay based on how often agents are used and how complex each interaction is. Copilot Credits are the billing units that measure AI activity, including interpreting content, taking actions, and generating responses. Each Copilot Credit is priced at $0.01. The number of credits consumed depends on agent design, usage volume, and the specific tasks performed.
Some AI agent capabilities are available through Business Central configuration, but AI interactions themselves draw from Copilot Credits. This means cost is driven by real usage, not by simply turning an agent on. Organizations can manage spend by controlling which agents are active, how often they run, and which actions require human approval. Custom AI agents built with Copilot Studio follow the same model, using Copilot Credits based on the complexity and frequency of their actions.
Scenario 1: Sales Order Agent
The Sales Order Agent processes customer requests received by email and performs several AI-driven steps to prepare a sales quote or order. Each step consumes Copilot Credits based on the type of AI interaction.
A typical Sales Order Agent flow includes:
- Analyze incoming email: 2 Copilot Credits
- Check item availability: 5 Copilot Credits
- Create or update a sales quote or sales order: 5 Copilot Credits
- Generate a response email: 2 Copilot Credits
- Process email attachment with usable sales data (50% of emails): 5 Copilot Credits
Total per request (average):
2 + 5 + 5 + 2 + (5 × 0.5) = 16.5 Copilot Credits
Monthly usage example:
- 100 customer requests per month
- Average of 16.5 Copilot Credits per request
Monthly Copilot Credit usage:
16.5 × 100 = 1,650 Copilot Credits
Estimated monthly cost:
1,650 × $0.01 = $16.50 per month
Actual cost will vary based on email volume, attachment frequency, and whether quotes are converted to orders.
Scenario 2: Payables Agent
The Payables Agent processes vendor invoices received by email and prepares draft purchase invoices for review. Credit usage is driven by invoice-level processing and the number of invoice lines interpreted.
A typical Payables Agent flow includes:
- Process vendor invoice and create purchase document draft:
10 agent actions × 5 credits = 50 Copilot Credits - Process invoice lines (average of 3 lines):
3 × 5 credits = 15 Copilot Credits
Total per invoice:
50 + 15 = 65 Copilot Credits
Monthly usage example:
- 100 vendor invoices per month
- Average of 3 invoice lines per invoice
Monthly Copilot Credit usage:
65 × 100 = 6,500 Copilot Credits
Estimated monthly cost:
6,500 × $0.01 = $65.00 per month
Emails without valid PDF invoice attachments do not consume Copilot Credits.
Get started with AI agents in Business Central
Getting started with AI agents in Business Central is most effective when guided by practical experience with ERP processes and real operational data. Rand Group works with organizations to evaluate existing workflows, transaction volumes, and pain points to identify where AI agents can deliver meaningful impact. This includes assessing finance, supply chain, and operational scenarios where automation can reduce manual effort without introducing unnecessary risk or complexity.
Rand Group also helps design a sustainable foundation for AI agents in Business Central. This includes configuring agents within Business Central and the Power Platform, defining approval and governance models, and ensuring agents align with existing controls and compliance requirements. As needs evolve, Rand Group supports extending Business Central with custom or industry-specific AI agents and provides ongoing optimization and support to keep agents accurate, reliable, and aligned with business goals.
Rand Group services for AI agents in Business Central include:
- Identifying high-impact agent opportunities based on business processes and data patterns
- Designing and configuring AI agents within Business Central and the Power Platform
- Extending Business Central with custom or industry-specific AI agents
- Providing ongoing optimization, governance, and long-term support
For teams that want structured, hands-on learning before implementation, Rand Group offers AI workshops focused on Microsoft Copilot, AI agents, and real Business Central use cases.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
- What are AI agents in Business Central?
AI agents in Business Central are intelligent software agents that monitor data, interpret context, and take or recommend actions within the ERP system. They operate alongside users to handle routine, high-volume tasks while supporting informed decision-making. - How are AI agents in Business Central priced?
AI agents in Business Central use a consumption-based pricing model based on Copilot Credits. Each AI interaction, such as analyzing content, taking an action, or generating a response, consumes credits based on task complexity, with Copilot Credits priced at $0.01 each. Total cost depends on how often agents run and which actions they perform, rather than a fixed per-agent license fee. - What is the difference between AI agents and automation in Business Central?
Traditional automation in Business Central relies on fixed rules and predefined workflows. AI agents go further by using data patterns and context to adapt their behavior, handle exceptions, and make recommendations when conditions change. - Are AI agents the same as Copilot in Business Central?
Copilot focuses on conversational assistance and user interaction, such as answering questions or summarizing information. AI agents work in the background to monitor data and execute or suggest actions based on events and conditions. - Are AI agents available out of the box in Business Central?
Some AI agents are delivered by Microsoft for specific scenarios, such as sales and payables processes. Additional agents can be created or extended using the Power Platform to meet specific business needs. - Are AI agents included with my Business Central license?
AI agents are enabled through Business Central configuration, but AI-driven actions consume Copilot Credits. Some functionality is available out of the box, while usage-based AI costs are billed separately based on consumption. - Do AI agents replace users or support them?
AI agents support users rather than replace them. They reduce manual effort by handling routine work while keeping people in control of approvals, exceptions, and final decisions. - How secure are AI agents in Business Central?
AI agents follow the same security, permissions, and compliance models as Business Central and the Power Platform. They respect role-based access, data security policies, and audit requirements. - Can AI agents be customized for specific industries or processes?
AI agents can be tailored using tools like Copilot Studio, AI Builder, and Power Automate to support industry-specific workflows and unique operational processes within Business Central. - How do organizations prepare to use AI agents in Business Central?
Organizations often start by building a practical understanding of Microsoft Copilot, AI agents, and governance considerations. Rand Group offers AI workshops that provide hands-on experience with AI inside Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365 using real business scenarios.
Next steps
AI agents in Business Central represent a shift from static automation toward systems that can monitor activity, respond to change, and assist users at scale. When implemented thoughtfully, they reduce manual workload while preserving oversight, security, and accountability across ERP processes.
To evaluate where AI agents make sense in your Business Central environment, contact Rand Group to discuss practical use cases, design considerations, and a structured path to adoption.